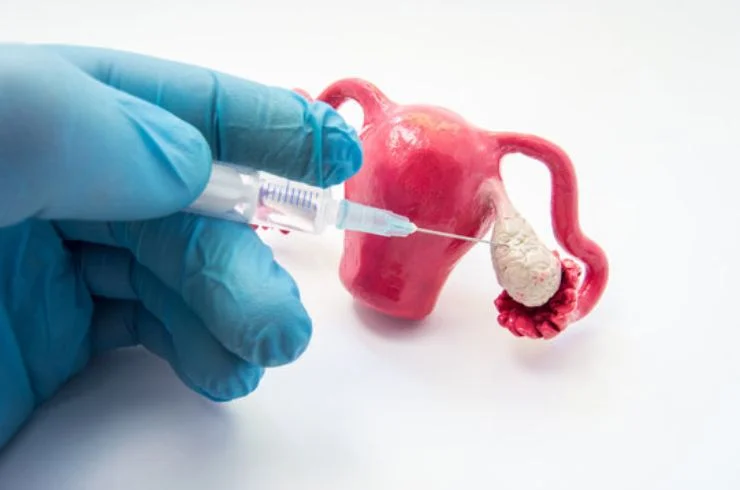
Ovulation induction (OI) is a commonly used fertility treatment that involves administering fertility medications to stimulate the ovaries to release one or more eggs. This process is particularly beneficial for women who face challenges with ovulation, either due to irregular or absent menstrual cycles. By using these medications, OI helps to regulate the ovulatory process, enabling the release of eggs, which is crucial for conception.
When is Ovulation Induction Recommended?
OI may be recommended in two specific scenarios:
How Does Ovulation Induction Work?
The OI process begins with a thorough evaluation of the patient’s hormonal profile and ovulatory function. Depending on the diagnosis, medications such as Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid) or Gonadotropins may be prescribed to stimulate the ovaries.
Throughout the OI cycle, patients undergo ultrasound monitoring and blood tests to track follicle development and hormone levels. Once the follicles have matured, an hCG injection (human chorionic gonadotropin) is administered to trigger the release of the egg(s), which is followed by timed intercourse or other fertility treatments like IUI or IVF.
Risks and Considerations
While OI is generally safe, there are a few risks associated with the treatment, including: